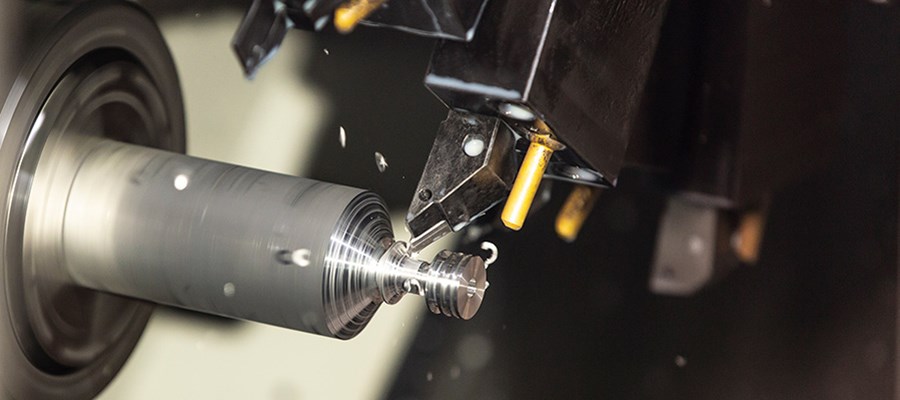
Carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composites exhibit better specific strength and stiffness than metals, but are prone to fatigue failure. The market value of carbon fiber-reinforced resin matrix composites could reach $31 billion in 2024, but the cost of a structural health monitoring system to detect fatigue damage could be upwards of $5.5 billion.
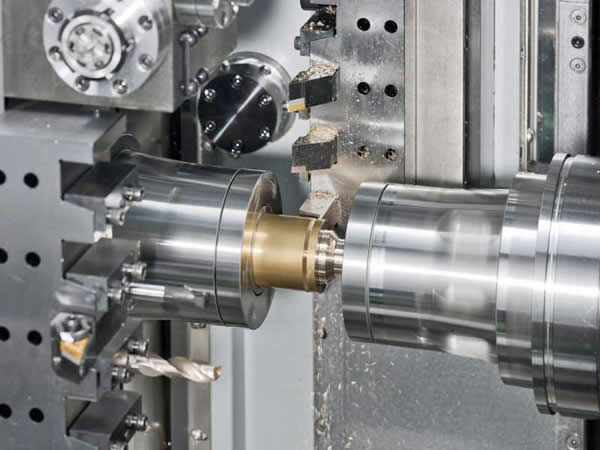
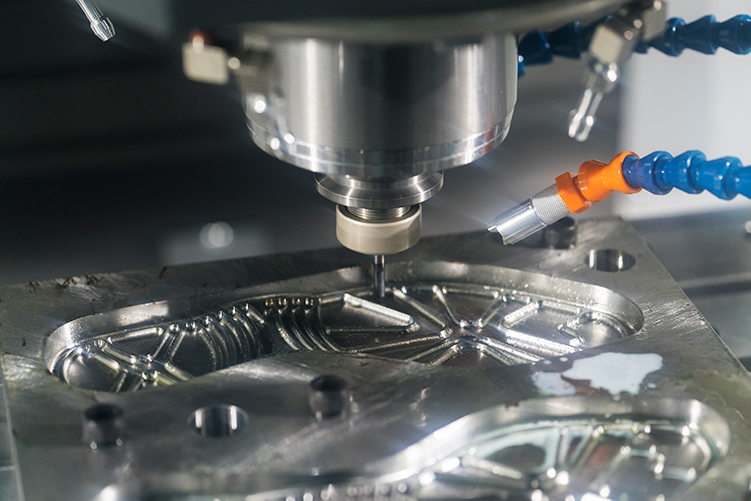


To address this problem, researchers are exploring nano-additives and self-healing polymers to stop cracks from propagating in materials. In December 2021, researchers at Washington University's Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and Beijing University of Chemical Technology proposed a composite material with a glass-like polymer matrix that can reverse fatigue damage. The matrix of the composite is composed of conventional epoxy resins and special epoxy resins called vitrimers. Compared with ordinary epoxy resin, the key difference between vitrifying agent is that when heated above the critical temperature, a reversible cross-linking reaction occurs, and it has the ability to repair itself.
Even after 100,000 damage cycles, fatigue in composites can be reversed by periodic heating to a time just above 80°C. In addition, exploiting the properties of carbon materials to heat up when exposed to RF electromagnetic fields can replace the use of conventional heaters for selectively repairing components. This approach addresses the "irreversible" nature of fatigue damage and can reverse or delay composite fatigue-induced damage almost indefinitely, extending the life of structural materials and reducing maintenance and operating costs.
CARBON / SILICON CARBIDE FIBER CAN WITHSTAND 3500 ° C ULTRA-HIGH TEMPERATURE
NASA's "Interstellar Probe" concept study, led by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, will be the first mission to explore space beyond our solar system, requiring travel at faster speeds than any other spacecraft. Far. To be able to reach very long distances at very high speeds, interstellar probes may need to perform an "Obers maneuver," which would swing the probe close to the sun and use the sun's gravity to catapult the probe into deep space.
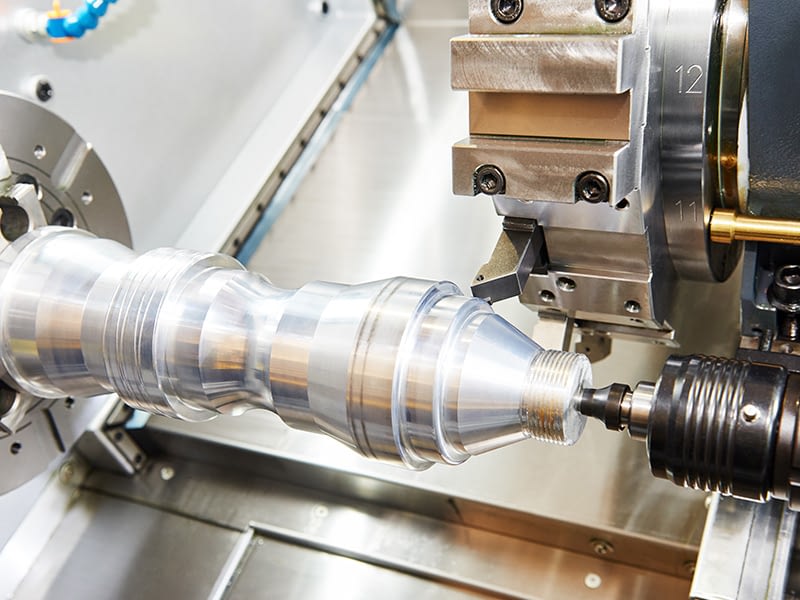


To achieve this goal, a lightweight, ultra-high temperature material needs to be developed for the detector's solar shield. In July 2021, American high-temperature materials developer Advanced Ceramic Fiber Co., Ltd. and the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory collaborated to develop a lightweight, ultra-high temperature ceramic fiber that can withstand high temperatures of 3500°C. The researchers converted the outer layer of each carbon fiber filament into a metal carbide such as silicon carbide (SiC/C) through a direct conversion process.
The researchers tested the samples using flame testing and vacuum heating, and these materials showed the potential of lightweight, low vapor pressure materials, extending the current upper limit of 2000°C for carbon fiber materials, and maintaining a certain temperature at 3500°C. Mechanical strength, it is expected to be used in the solar shield of the probe in the future.

Post time: Jul-18-2022
